Surgical separation of a multirooted tooth through the furcation area is a specialized procedure used to divide a tooth with multiple roots into individual roots. This intricate technique offers unique advantages in certain clinical scenarios, making it an essential tool in the armamentarium of dental surgeons.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of surgical separation, exploring its indications, techniques, instrumentation, post-operative care, and long-term outcomes. By providing a thorough understanding of this procedure, we empower dental professionals to make informed decisions and deliver optimal patient care.
1. Definition and Overview
Surgical separation of a multirooted tooth through the furcation area is a dental procedure that involves dividing a multirooted tooth into separate roots. This procedure is typically performed when a tooth is severely damaged or decayed, and other treatment options, such as root canal therapy, are not feasible.
The furcation area is the region where the roots of a multirooted tooth meet.
Indications and Limitations
Surgical separation of a multirooted tooth is indicated in cases where:
- The tooth is severely damaged or decayed and cannot be restored with conventional methods.
- The tooth has a large furcation involvement that cannot be adequately treated with root canal therapy.
- The tooth has a vertical root fracture that extends into the furcation area.
Limitations of surgical separation include:
- The procedure is technically demanding and requires specialized training and experience.
- The procedure can be time-consuming and may require multiple appointments.
- The procedure can be associated with complications, such as root damage, nerve injury, and infection.
- Administer local anesthesia to numb the area around the tooth.
- Create a surgical flap to expose the furcation area.
- Carefully separate the roots of the tooth using a surgical instrument, such as a chisel or osteotome.
- Remove any remaining root fragments or debris.
- Smooth the edges of the roots and prepare them for restoration.
- Close the surgical flap and suture the incision.
- Surgical scalpel
- Surgical scissors
- Surgical chisel
- Osteotome
- Root elevators
- Dental bur
- Dental handpiece
- Suture material
- Taking pain medication as prescribed.
- Rinsing the mouth with a saltwater solution several times a day.
- Eating soft foods and avoiding chewing on the surgical site.
- Avoiding smoking and alcohol consumption.
- Root damage
- Nerve injury
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Failure of the roots to separate
- Surgical separation can save a tooth that would otherwise need to be extracted.
- The procedure can improve the long-term prognosis of the tooth.
- The procedure can be used to treat a variety of dental problems.
- The procedure is technically demanding and requires specialized training and experience.
- The procedure can be time-consuming and may require multiple appointments.
- The procedure can be associated with complications.
2. Techniques and Procedures: Surgical Separation Of A Multirooted Tooth Through The Furcation Area
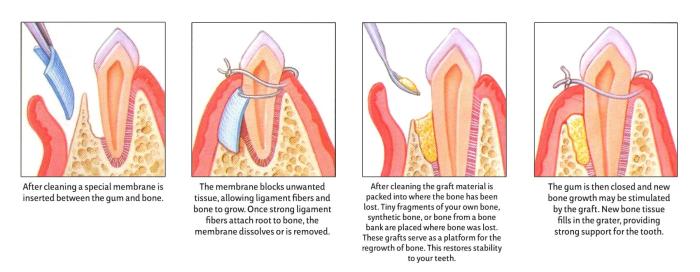
There are several different surgical techniques that can be used to separate multirooted teeth. The choice of technique depends on the specific case and the surgeon’s preference.
Step-by-Step Instructions, Surgical separation of a multirooted tooth through the furcation area
3. Instrumentation and Materials
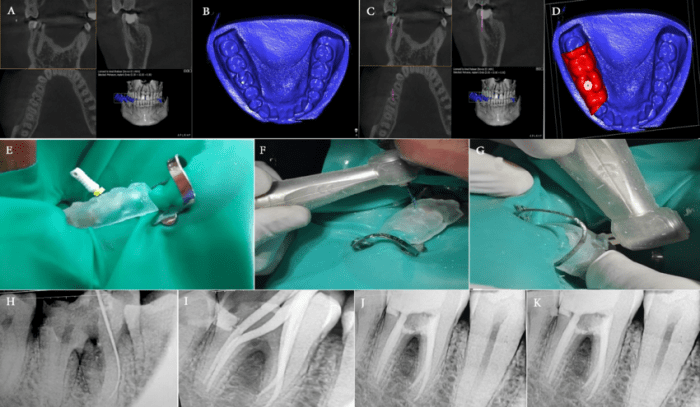
The following instruments and materials are typically used for surgical separation of multirooted teeth:
4. Post-Operative Care and Management
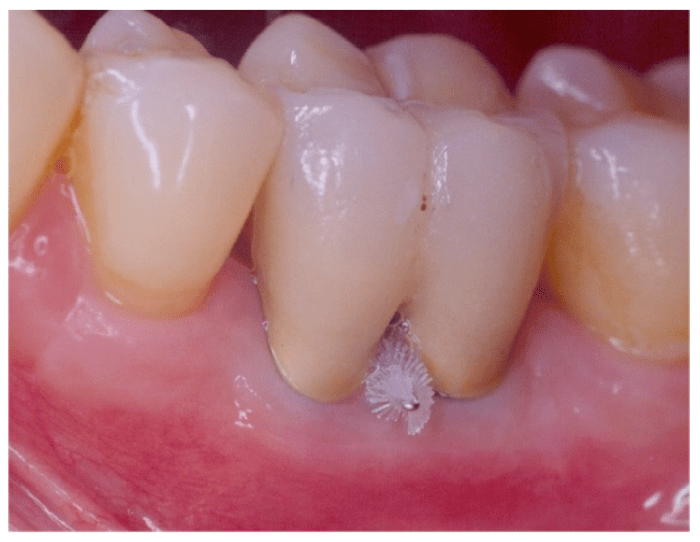
After surgical separation of a multirooted tooth, it is important to follow the post-operative care instructions provided by the surgeon. These instructions typically include:
The surgeon will typically schedule follow-up appointments to monitor the healing process and to remove the sutures.
Potential Complications
Potential complications of surgical separation of multirooted teeth include:
5. Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages
Disadvantages
Commonly Asked Questions
What are the indications for surgical separation of multirooted teeth?
Surgical separation is indicated when non-surgical approaches, such as endodontic treatment or root canal therapy, are not feasible or have failed. It may also be necessary to separate roots prior to orthodontic treatment or to facilitate the removal of impacted teeth.
What are the different surgical techniques used for multirooted tooth separation?
The most common techniques include the vertical osteotomy, horizontal osteotomy, and the combined vertical-horizontal osteotomy. The choice of technique depends on the specific anatomy of the tooth and the clinical situation.
What are the potential complications of surgical separation?
Potential complications include bleeding, infection, damage to adjacent teeth or structures, and failure of the separation. Proper patient selection, meticulous surgical technique, and appropriate post-operative care can minimize these risks.